Removing OEM Partition: Delete OEM Partition Windows 10 and Fully Remove OEM Partition Safely
When navigating the complexities of Windows 10, users often encounter an obscure element known as the OEM partition. This partition, usually hidden from casual view, serves a vital role in system recovery and manufacturer customization. However, it can sometimes become a nuisance, particularly when storage space is at a premium. This article provides a comprehensive guide on how to delete the OEM partition safely, ensuring that users can fully reclaim valuable disk space without compromising system integrity. Whether you're aiming to optimize storage or customize your system further, understanding the intricacies of OEM partitions and the methods for their removal is essential.
In this article, you will find out:
- what is OEM partition
- should you or shouldn't delete it
- how DiskInternals Partition Recovery can help you
Are you ready? Let's read!
Urgent Facts: Why the OEM Partition Exists and When You Must Delete It
The OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) partition is a dedicated section on your hard drive set aside by your device’s manufacturer. Its primary purpose is to store system recovery and diagnostic tools, alongside software that is specific to your device brand. While the partition is crucial for restoring your computer to its factory settings during troubleshooting, there are scenarios where deleting it may be necessary. For users aiming to optimize storage space or transition to a cleaner system configuration, understanding the implications of removing this partition is vital.
OEM Partition Windows 10 — What It Holds and Why It Consumes Space
Within the confines of the OEM partition, you will find a collection of files designed to revert your system to its out-of-the-box state. These include recovery tools that kick in during system failures, proprietary drivers, and occasionally, bundled software from the manufacturer. Although these elements ensure the functionality and quick recovery of your device, they also consume valuable disk space — sometimes several gigabytes, which could otherwise be used to store personal files or improve system performance.
Risk Snapshot: Firmware Bricks, Boot Loops, Hidden Malware
Attempting to delete the OEM partition carries certain inherent risks. One such risk includes bricking the firmware, which can render your device inoperable. Boot loops might become a persistent issue if crucial recovery files are removed, leading to continuous restarts without successfully booting the system. Moreover, there's a potential for hidden malware to exploit the deletion process, embedding itself within system files or other partitions left unprotected post-deletion. These hazards underline the importance of considering if, and when, removing the OEM partition is necessary.
Backup OEM Partition Before Any Action — Two Fast Methods
Before you consider removing the OEM partition, it’s crucial to back it up to safeguard against potential data loss or system malfunctions. Two efficient methods to perform this are:
- 1. Windows Disk Management:
- Utilize the built-in Disk Management tool in Windows 10. You can search for 'Disk Management' in your Start menu, identify the OEM partition, and create a backup using system tools.
- This method is straightforward and requires no external software, making it ideal for users who prefer using native Windows utilities.
- 2. Third-Party Software:
- Employ a reputable third-party tool specifically designed for partition management, such as DiskInternals Partition Recovery.
- This tool often offers more features and flexibility, providing options to clone partitions, manage backups, or even automate the backup process.
Core Solution: How to Delete OEM Partition on Hard Drive Without Data Loss
Deleting the OEM partition on your Windows 10 machine can free up precious disk space, but doing so safely requires meticulous steps to prevent data loss and system errors. Below, we explore effective methods that leverage both command-line tools and graphical interfaces, as well as precautionary measures for secure removal.
Remove OEM Partition Windows 10 via DiskPart (Step-by-Step)
DiskPart is a powerful command-line utility in Windows that allows advanced users to manage disk partitions directly. Here’s how to safely remove an OEM partition:
- 1. Open Command Prompt as an Administrator:
- Press
Win + Xand select "Command Prompt (Admin)" or "Windows PowerShell (Admin)".
- 2. Launch DiskPart:
- Type
diskpartand press Enter.
- 3. List Disks and Select Your Disk:
- Enter
list diskto display all available disks. - Type
select disk X, replacing "X" with the disk number where the OEM partition resides.
- 3. List and Select Partitions:
- Use
list partitionto display partitions on the selected disk. - Identify the OEM partition and type
select partition Y, replacing "Y" with the corresponding number.
- 4. Delete the OEM Partition:
- Type
delete partition overrideand press Enter. - This command ensures the partition is removed even if it is protected.
Windows 10 Delete OEM Partition with Disk Management GUI
For those preferring a graphical interface, the Disk Management tool provides an intuitive way to manage partitions. Here's how to use it:
- 1. Access Disk Management:
- Right-click on the Start menu and select "Disk Management."
- 2. Identify the OEM Partition:
- Locate the OEM partition, typically labeled as "OEM" or "Recovery."
- 3. Delete the Partition:
- Right-click on the OEM partition and select "Delete Volume."
- Confirm the action when prompted. This will remove the partition and free up the space.
Create Partition Recovery Software OEM Image as a Safety Net
Before deleting the OEM partition, creating a recovery image is a failsafe operation. This ensures that you can restore any lost functionality or files afterward. Here's a simple way to set it up:
- 1. Select Reliable Recovery Software:
- Choose trusted software like Macrium Reflect or Acronis True Image.
- 2. Create a Full Backup:
- Open the software and select the disk containing the OEM partition.
- 3. Save the Backup Image:
- Schedule a task to create a backup image of the entire disk or just the OEM partition.
- Store this image on an external drive or cloud storage for easy access later.
Enhanced Approach: Partition Recovery™ by DiskInternals for Post-Deletion File Rescue
When handling delicate operations like OEM partition removal, even the most cautious steps can sometimes lead to unintentional data loss. DiskInternals' Partition Recovery™ offers a robust solution for rescuing lost files, providing peace of mind as you navigate post-deletion scenarios.
Instant Scan: Recover Files Lost During OEM Removal
Partition file recovery tool is equipped with an "Instant Scan" feature that swiftly identifies and retrieves files lost during the OEM partition removal process. Here's how it ensures your data stays safe:
Use the step-by-step instructions for DiskInternals Partition Recovery described below and very soon the partition will be restored.
Step 1. Download and install the trial version of Partition Recovery.
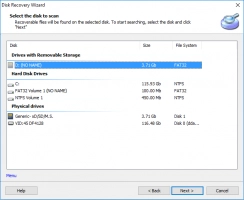
Step 2. Select the disk and the wizard mode: “reader”, “uneraser” or “recovery”. To restore the OEM partition, it is recommended to select the “recovery” mode.
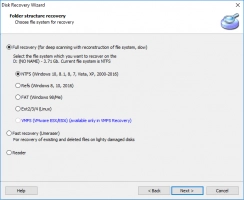
Step 3. Select the type of files you want to recover. If you wish, you can skip this step.
Step 4. Scan. Wait for the process to complete; it will take some time.
Step 5. Preview and restore. Right-click on the file and select "Preview in New Window." This way, you will be convinced of the quality of the recovered data.
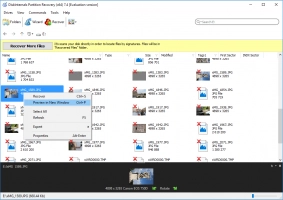
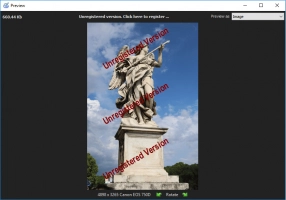
Step 7. Saving. Purchase a license and enter the license key in the required window. The restored partition is best saved in a new place.
You can use this method to recover any information from the sections. DiskInternals Partition Recovery and its developers will help you in all difficult situations.
Case Study — DiskInternals Campaign Saves a 256 GB SSD After Failed OEM Wipe
In a compelling case study, DiskInternals saved the day for a user attempting an OEM partition wipe on a 256 GB SSD. Here’s a glimpse into how the situation unfolded and was resolved:
A tech enthusiast attempted to free up space by removing the OEM partition to expand their storage capabilities. Unfortunately, during the process, crucial personal files were accidentally deleted, leaving the drive seemingly barren.
Turning to Partition Recovery™ by DiskInternals, the user initiated an "Instant Scan" which swiftly pinpointed the misplaced data. Within minutes, critical files were restored, averting what could have been a disappointing loss. This case underscores DiskInternals' efficacy in managing recovery operations post-partition deletion, providing users with reliable tools to recover from unintended errors.
Whether a novice or experienced user, DiskInternals Partition Recovery™ offers an enhanced approach to safeguard your data integrity through potentially hazardous system modifications.
Learn how to:
Comparison Table: DiskPart vs Disk Management vs Partition Recovery™
| Feature | DiskPart | Disk Management | Partition Recovery™ |
| Interface Type | Command-Line | Graphical User Interface | Graphical User Interface |
| Primary Function | Advanced Disk Partition Management | Basic Disk Partition Management | Data Recovery |
| Ease of Use | Requires Technical Knowledge | User-Friendly | User-Friendly |
| Partition Removal | Yes | Yes | No |
| Data Recovery | No | No | Yes |
| Speed | Fast | Moderate | Depends on Data Volume |
| Error Handling | Manual | Automatic Prompt for Common Errors | Automated Scan and Recovery |
| System Compatibility | Windows Only | Windows Only | Windows and Mac |
| Additional Features | Scripting and Automation | Limited to Basic Operations | File Preview, Deep Scan |
| Best Use Case | Advanced Users Needing Detailed Control | Users Seeking Ease of Access for Partition Tasks | Recovery of Lost Files |
Conclusion
In summary, each tool offers unique advantages depending on your specific needs and technical expertise. DiskPart is ideal for advanced users seeking detailed control over their partitions through command-line interaction, making it efficient for those comfortable with scripting and precise commands. In contrast, Disk Management provides a more user-friendly graphical interface, suitable for users seeking straightforward partition management for routine tasks without diving deep into complex options.
On the other hand, Partition Recovery™ by DiskInternals stands out as a specialized tool for data recovery, particularly useful when you need to restore lost or deleted files following partition modifications. Its intuitive interface, combined with powerful scanning capabilities, makes it an essential tool for recovering from errors that might occur during partition removal.
Ultimately, choosing between these solutions depends on your proficiency and the goals you aim to achieve. Whether you prioritize comprehensive control, ease of use, or safeguarding against data loss, understanding these tools' distinct strengths will guide you in effectively managing your storage and recovery tasks.
FAQ
How to Remove OEM Partition When “Delete” Is Greyed Out
- 1. Open Command Prompt as an Administrator:
- Press
Win + Xand select "Command Prompt (Admin)" or "Windows PowerShell (Admin)".
- 2. Launch DiskPart:
- Type
diskpartand press Enter to start the DiskPart utility.
- 3. List Available Disks:
- Type
list diskto show all connected disks. - Identify the disk number that contains the OEM partition.
- 4. Select the Disk:
- Enter
select disk X, replacing "X" with the disk number containing the partition.
- 5. List Partitions:
- Use
list partitionto view all partitions on the selected disk. - Identify the OEM partition you want to delete.
- 6. Select the OEM Partition:
- Type
select partition Y, replacing "Y" with the partition number.
- 7. Force Delete the OEM Partition:
- Enter
delete partition overrideand press Enter. - This command will remove the partition regardless of its protected status.
Can I Restore the OEM Partition After Deletion?
- 1. Use a Backup Image:
- If you created a backup image of the OEM partition using disk imaging software (like Macrium Reflect, Acronis True Image, or similar tools) before deleting it, you can restore it from this image.
- Load the backup software, select the drive or partition to restore the image to, and follow the instructions to complete the restoration process.
- 2. Factory Reset/Recovery Media:
- Access the factory recovery media that came with your device. Many manufacturers provide recovery disks or USB drives that can restore the computer to its factory state, including recreating the OEM partition.
- Insert the recovery media and boot from it (you may need to change boot order settings in BIOS/UEFI to do this) and follow the on-screen instructions to restore your system.
- 3. Contact Manufacturer Support:
- If you did not create a backup or do not have recovery media, contacting the device manufacturer may offer a solution. They can sometimes provide or guide you to official recovery options or media.
Action Plan: Free Trial Download of DiskInternals Partition Recovery™
- 1. Initiate the Free Trial Download:
- Click on the option for the free trial download of Partition Recovery™.
- Follow the prompts to start downloading the installation file to your computer.
- 2. Install the Software:
- Once the download is complete, locate the installation file (usually in your "Downloads" folder) and double-click it to start the installation process.
- Follow the on-screen instructions to install the software. You might need administrative privileges to complete this step.
- 3. Launch DiskInternals Partition Recovery™:
- After installation, open the software. This can usually be done from the Start menu or a desktop shortcut.
- 4. Explore Features:
- Use the trial version to explore its functionality. You can often perform scans and preview recoverable files with a trial.
- Familiarize yourself with options such as quick scan, deep scan, and file preview to understand the capabilities of the recovery tool.
- 5. Evaluate and Decide:
- Try out the software under trial conditions and evaluate its performance for your specific needs.
- Decide whether the full version might be necessary based on the trial experience.
