How to Recover Files from an Unallocated Partition
Here you will find out:
- what unallocated partitions are
- what the reasons for it
- how DiskInternals can help you
Are you ready? Let's read!
About unallocated space and partitions on the disk
Any user should understand that unallocated space is not just free disk space, but an area that is not free of any particular volume. And it’s so easy to use it to save files.
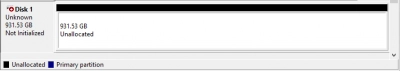
To do this, first, this space must be included in one of the sections to allocate this free space.
When you may need to recover an unallocated partition
When removing one or more partitions on a drive in Windows 10, you will need to restore an unallocated partition in case you require the data on these partitions and you weren't planning to delete them at all. In other words, it's possible that the deletion was made by mistake.
Then immediately start the process of recovering the data from the unallocated partition.
What Does It Mean When a Hard Drive Is Unallocated?
When a hard drive is "unallocated," it means that the space on the drive has not been partitioned or formatted for use. In other words, the hard drive does not have any defined partitions or file systems.
Here are a few possible reasons for a hard drive being unallocated:
1. New or Uninitialized Drive: When you purchase a new hard drive or connect a previously unused drive to your computer, it may appear as unallocated because it has not been initialized or partitioned yet. In such cases, you need to initialize the drive and create partitions before you can use it.
2. Accidental Deletion of Partitions: If you or someone else accidentally deleted the partitions on the hard drive, it will show up as unallocated. This can happen during disk management operations, such as repartitioning, formatting, or using disk management tools.
3. Corrupted or Damaged Partition Table: A corrupted or damaged partition table can result in an unallocated hard drive. The partition table contains information about the partitions on the drive, and if it gets damaged or corrupted, the partitions may become inaccessible, leading to an unallocated status.
4. Disk Errors or Malfunction: Disk errors or malfunctions can cause the partition information to become corrupted or lost, resulting in an unallocated hard drive. This can happen due to various factors, such as power failures, improper shutdowns, hardware issues, or software conflicts.
5. Malicious Activity or Virus Attack: In some cases, malicious activities or virus attacks can target the partition table or file system structures, causing them to become corrupted or deleted. This can lead to the hard drive being shown as unallocated.
Reasons for unallocated partitions
Your disk may become unallocated at the most inopportune moment and this may happen due to a number of external and internal factors.
For example, if you do not make timely updates to the system and drivers, this can not only harm the computer but also result in the appearance of an unallocated disk. Any system errors, bad sectors, file system errors — all these are potential threats to you.
And if you also encounter an unallocated disk, then you need to know what to do in this situation.
How to recover unallocated partition with DiskInternals
Recover data from unallocated space can be done quickly and painlessly for you by DiskInternals Partition Recovery.
It uses a deep disk scanning system and can recover a large amount of information (up to 1 Pb). This application restores everything: music, documents, images, videos, etc. The software works even with damaged file systems, including HFS, NTFS, XFS, Ext2 / 3/4, ReiserFS, FAT12, ReFS, Reiser4, etc. It works smoothly with Windows 7, 8, 10, etc.
There is a free full-featured trial version of the application, which you can download right now and see the results for free (using the Preview function).
1. Download DiskInternals Partition Recovery
After downloading, proceed to begin the process of recovering data from an unallocated partition.
Recovery Wizard will start automatically.
2. Disk Selection
Then select the disk with an unallocated partition and choose the program mode (in your case, full recovery will be most helpful).
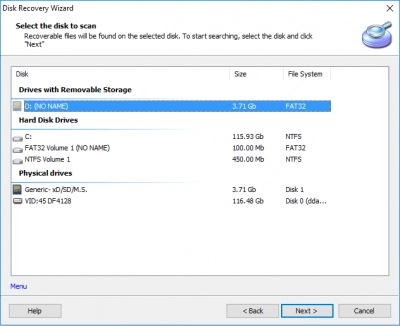
3. Disk Scanning
Sit back, as scanning can take some time. However, the search results will make you forget about it.
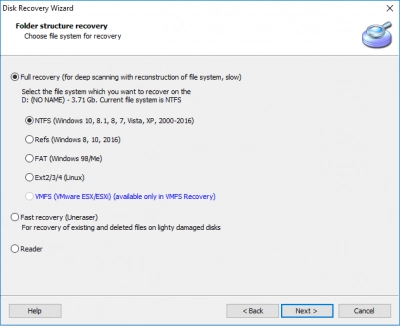
4. Reclaim Your Files
Now select the file you need, press Ctrl + P and preview it in a new window.
As soon as you are ready to export these files, buy a license and export them where you want them to go (of course, it is best that they not go back to their original location).
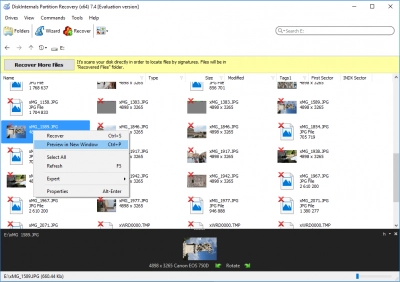
Then you can exit the program and enjoy your files.
Be sure to remember that, the faster you start restoring an unallocated partition, the more pleasant the result will be. These are not empty words since rewriting can harm the whole process. Therefore, you need to think quickly and sensibly.
How to Recover Data from an Unallocated Space With System Tools
Check Your System for Existing Backup and Restore
Recovering data from an unallocated space using system tools depends on whether you have an existing backup available. Here are the steps to check for backups and perform a restore:
1. Check for System Backup: First, check if your system has a backup feature enabled and if any backups exist. This can include built-in backup tools like File History on Windows or Time Machine on macOS. Open the respective backup tool and check for available backups that include the data you want to recover.
2. Restore from System Backup: If you have a backup available, follow the instructions provided by the backup tool to restore the data. Typically, you'll need to select the backup source and choose the files or folders you want to restore. Make sure to select the desired location to restore the files, which should not be the unallocated space.
Fix unallocated hard drive with CMD
To fix an unallocated hard drive using the Command Prompt (CMD), you can try the following steps:
1. Press the Windows key on your keyboard, type "CMD," and open the Command Prompt as an administrator.
2. In the Command Prompt window, type "diskpart" and press Enter. This will launch the DiskPart utility, which allows you to manage disks and partitions.
3. Type "list disk" and press Enter. This will display a list of all the disks connected to your computer. Identify the unallocated hard drive by its size and make a note of its disk number.
4. Type "select disk X" (replace X with the disk number of the unallocated drive) and press Enter. This selects the unallocated disk for further operations.
5. Type "create partition primary" and press Enter. This will create a new primary partition on the unallocated space.
6. Type "format quick" and press Enter. This will quickly format the newly created partition with the default file system (usually NTFS).
7. After the format is complete, type "assign letter=X" (replace X with the desired drive letter) and press Enter. This assigns a drive letter to the newly formatted partition.
8. Close the Command Prompt.
Once these steps are completed, the unallocated hard drive should now be allocated and formatted with a drive letter assigned to it. You should be able to access the drive and use it for storing data.
It's important to note that these steps will erase any existing data on the unallocated drive. If you have important data on the drive, it's recommended to perform data recovery before attempting these steps or seek professional assistance to avoid data loss.
Additionally, if the unallocated hard drive is experiencing physical issues, software solutions may not be effective. In such cases, it's advisable to consult a professional data recovery service or a technician for further assistance.
FAQ
How do I recover an unallocated partition?
1. Download and Install DiskInternals Partition Recovery: Go to the DiskInternals website and download the Partition Recovery software. Install it on your computer.
2. Launch DiskInternals Partition Recovery: Open the software from the Start menu or desktop shortcut.
3. Select the Affected Drive: In the DiskInternals Partition Recovery window, you'll see a list of available drives and partitions. Select the unallocated drive or disk that contained the lost partition.
4. Start the Scan: Click on the "Next" button to begin the scanning process. DiskInternals Partition Recovery will scan the unallocated space to search for lost or deleted partitions.
5. Scan and Analysis Process: The software will perform a thorough scan and analysis of the unallocated space. This may take some time depending on the size of the drive and the complexity of the partition structure.
6. Preview and Select the Lost Partition: Once the scan is complete, DiskInternals Partition Recovery will display a list of recoverable partitions. You can preview the found partitions and their contents to verify if they are the ones you want to recover. Select the desired partition for recovery.
7. Save Recovered Partition: Choose a safe location on a different drive or storage device to save the recovered partition and its files. It's crucial not to save it to the same unallocated space or drive from which you are recovering.
8. Complete the Recovery Process: Click on the "Next" button to begin the recovery process. DiskInternals Partition Recovery will recreate the partition and restore the files to the specified location.
9. Access Recovered Partition: Once the recovery process is complete, you can access the recovered partition and its files from the specified location. You may need to assign a drive letter to the recovered partition using Disk Management in Windows.
What is an unallocated space partition?
An unallocated space partition refers to a section of a storage device, such as a hard drive or SSD, that has not been assigned to any specific partition or file system. It represents unused or free space on the storage device that is not currently allocated for data storage.
Unallocated space can occur in different scenarios:
1. New or Uninitialized Drive: When you purchase a new storage device or connect a new one to your computer, it may appear as unallocated because it has not been initialized or partitioned yet. In this case, you need to create partitions and allocate the space for data storage.
2. Deleted or Lost Partition: If a partition is deleted, lost, or becomes inaccessible due to software errors, accidental deletion, or other reasons, it may result in unallocated space on the drive. The partition information is no longer present, and the space becomes unallocated until it is reassigned or recovered.
3. Partitioning or Formatting Operations: During disk management operations, such as resizing partitions, formatting, or repartitioning, unallocated space can be created. When resizing or deleting partitions, the space is freed up and becomes unallocated until it is utilized for a new partition or merged with an existing one.
4. Disk Errors or Failures: Disk errors or failures can cause data corruption or damage to the partition table, leading to unallocated space. If the system cannot recognize the partition information, it may show the space as unallocated.
It's important to note that unallocated space does not contain any file system or data. To make use of unallocated space, you need to create partitions, assign file systems, and allocate the space for storing files and data.
Before performing any operations on unallocated space, it's recommended to back up your important data and exercise caution to avoid data loss.
Can not create partitions from unallocated space?
If you're unable to create partitions from unallocated space, there could be a few possible reasons:
1. Disk Corruption or Physical Issues: If the storage device is experiencing physical issues or disk corruption, it may prevent you from creating partitions from unallocated space. In such cases, it's advisable to consult a professional data recovery service or a technician for further assistance.
2. Maximum Partition Limit: The partitioning process may fail if the number of existing partitions on the disk has reached the maximum limit allowed by the partitioning scheme. Different partitioning schemes have varying limits, such as the Master Boot Record (MBR) partitioning scheme allowing up to four primary partitions or three primary partitions and an extended partition. If the limit is reached, you'll need to delete or modify existing partitions to create new ones.
3. Disk Management Restrictions: The built-in Disk Management utility in Windows has certain limitations that may prevent the creation of partitions from unallocated space in specific scenarios. For example, it may restrict the creation of partitions on dynamic disks or certain types of removable storage devices. In such cases, you can try using third-party partitioning tools that offer more advanced features and flexibility.
4. File System Incompatibility: If the unallocated space is located on a disk with an incompatible file system, it may prevent the creation of partitions. For example, if the unallocated space is on a disk with a file system not supported by the operating system, you may encounter difficulties creating partitions. Ensure that the disk is formatted with a compatible file system.
5. Insufficient Privileges: Creating partitions typically requires administrative privileges. Ensure that you are logged in as an administrator or have the necessary permissions to perform partitioning operations.
How do I extend unallocated space?
1. Press the Windows key + X on your keyboard and select "Disk Management" from the menu that appears. This will open the Disk Management utility.
2. In the Disk Management window, locate the partition that you want to extend. It should be adjacent to the unallocated space.
3. Right-click on the partition and select "Extend Volume." This will open the Extend Volume Wizard.
4. In the Extend Volume Wizard, click "Next" to proceed.
5. On the "Select Disks" page, you'll see the available space to extend the partition. Ensure that the unallocated space is listed.
6. Specify the amount of space you want to add to the partition by entering the desired value in the "Select the amount of space in MB" field. Alternatively, you can leave it as the maximum value to use the entire unallocated space.
7. Click "Next" and review the summary of the operation. Ensure that everything looks correct.
8. Click "Finish" to start the process of extending the partition. The process may take some time depending on the size of the partition and the speed of your storage device.
How do I merge partitions?
To merge partitions in Windows using the built-in Disk Management tool, follow these steps:
Note: Merging partitions will result in the loss of data on the selected partitions. Make sure to back up any important data before proceeding.
1. Press the Windows key + X on your keyboard and select "Disk Management" from the menu that appears. This will open the Disk Management utility.
2. In the Disk Management window, identify the partitions you want to merge. They should be adjacent to each other and have unallocated space in between.
3. Right-click on the partition that you want to extend and select "Delete Volume." This will remove the partition and turn it into unallocated space.
4. Right-click on the other partition that you want to merge with the unallocated space and select "Extend Volume." This will open the Extend Volume Wizard.
5. In the Extend Volume Wizard, click "Next" to proceed.
6. On the "Select Disks" page, you'll see the available space to extend the partition. Ensure that the unallocated space resulting from the deleted partition is listed.
7. Specify the amount of space you want to add to the partition by entering the desired value in the "Select the amount of space in MB" field. Alternatively, you can leave it as the maximum value to use the entire unallocated space.
8. Click "Next" and review the summary of the operation. Ensure that everything looks correct.
9. Click "Finish" to start the process of extending the partition. The process may take some time depending on the size of the partition and the speed of your storage device.
Once the process is complete, the selected partitions will be merged, with the unallocated space added to the remaining partition. You can verify the changes by checking the Disk Management window or using file explorer to view the updated size of the partition.
Keep in mind that merging partitions will result in the loss of data on the deleted partition. Ensure that you have backed up any important data before performing these operations. If you encounter any issues or limitations with the Disk Management tool, you may need to consider using third-party partitioning software that offers more advanced features and flexibility.
How do I assign unallocated space to C drive?
To assign unallocated space to the C drive in Windows using the built-in Disk Management tool, follow these steps:
Note: Assigning unallocated space to the C drive involves extending the partition, which may result in the loss of data. Make sure to back up any important data before proceeding.
1. Press the Windows key + X on your keyboard and select "Disk Management" from the menu that appears. This will open the Disk Management utility.
2. In the Disk Management window, locate the C drive partition. It is usually labeled as "C:" and has the operating system installed.
3. Right-click on the C drive partition and select "Extend Volume." This will open the Extend Volume Wizard.
4. In the Extend Volume Wizard, click "Next" to proceed.
5. On the "Select Disks" page, you'll see the available space to extend the C drive. Ensure that the unallocated space is listed.
6. Specify the amount of space you want to add to the C drive by entering the desired value in the "Select the amount of space in MB" field. Alternatively, you can leave it as the maximum value to use the entire unallocated space.
7. Click "Next" and review the summary of the operation. Ensure that everything looks correct.
8. Click "Finish" to start the process of extending the C drive. The process may take some time depending on the size of the partition and the speed of your storage device.
Once the process is complete, the unallocated space will be assigned and added to the C drive partition, effectively extending its size. You can verify the changes by checking the Disk Management window or using file explorer to view the updated size of the C drive.
Remember to back up your data before making any changes to your partitions to avoid potential data loss. If the Extend Volume option is not available or you encounter any limitations with the Disk Management tool, you may need to consider using third-party partitioning software that offers more advanced features and flexibility.
