Recovering Deleted Folders in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide
Folders serve as organizational tools for sorting various types of files on your computer. For instance, you might have one folder dedicated to music and another for videos or movies. Similarly, you could have a separate folder for your business documents. The system can be as detailed as you'd like.
However, it's crucial to recognize that folders are not immune to accidental deletions or losses—just like individual files. When you inadvertently delete a folder, the ramifications are greater since you're erasing multiple files at once, not just one.
The silver lining here is that, much like individual lost or deleted files can often be recovered, so can entire folders, whether you're using a Windows or macOS system. This article will guide you through the process of restoring deleted folders on your computer.
Understanding Folder Deletion in Windows 10
Common Causes of Accidental Folder Deletion
Accidental deletion of folders in Windows 10 can occur due to a variety of reasons, often rooted in everyday user interactions and occasional technical glitches:
- User Errors: One of the most common causes is human error. This can include accidentally clicking "delete" instead of another nearby button, or using keyboard shortcuts like "Ctrl + X" and then failing to paste before closing a program, leading to unintentional data loss.
- Software Malfunctions: Occasionally, software applications may crash or behave unpredictably. Such malfunctions can result in unsaved work or even deleted files if the program corrupts data paths or mismanages open files during a crash.
- System Crashes: The stability of an operating system is crucial, but sometimes Windows 10 can encounter unexpected system crashes. When this happens, open folders and files may not be saved correctly, leading to loss or corruption.
- Virus and Malware Attacks: Malicious software can wreak havoc on your system, intentionally or unintentionally deleting files. Ransomware, for instance, can encrypt or remove folders until a ransom is paid. In less severe cases, viruses may accidentally damage files as they spread through the system.
Difference Between Temporary and Permanent Deletion
The way files are deleted on Windows 10 affects your ability to recover them. It's important to distinguish between temporary and permanent deletion to understand your recovery options:
- Temporary Deletion (Recycle Bin): When you delete a file using the "Delete" key or dragging it to the Recycle Bin, it isn't immediately erased from your hard drive. Instead, it is moved to the Recycle Bin, where it can be easily restored. Until the Recycle Bin is emptied, the file remains recoverable, providing a safe buffer against accidental deletions.
- Permanent Deletion (Shift + Delete): If you use the "Shift + Delete" command, the file bypasses the Recycle Bin and is directly marked for deletion by the operating system. This is considered a permanent deletion, as Windows removes pointers to the data on the disk, freeing up space for new data. Recovering such files requires specialized recovery software that can scan the disk for remnants of the deleted data, which hasn't yet been overwritten by new files.
Immediate Steps to Take After Deleting a Folder
Checking the Recycle Bin
One of the first actions you should take after deleting a folder is to check the Recycle Bin, as it often provides a straightforward way to recover deleted items:
- Navigate to the Recycle Bin: This icon is typically located on your desktop. Double-clicking the Recycle Bin will open it, allowing you to view its contents.
- Locate the Deleted Folder: Once inside the Recycle Bin, browse through the list of items to find the folder you accidentally deleted. You can use the search bar for quicker access if you remember the folder's name.
- Restore the Folder: After locating the folder, right-click on it and select "Restore." This action will move the folder back to its original location, restoring it just as it was before deletion.
Utilizing the "Undo Delete" Feature
If you realize the deletion immediately, the "Undo Delete" feature in Windows 10 offers a fast and efficient way to recover your folder:
- Keyboard Shortcut: Press "Ctrl + Z" immediately after deleting the folder. This keyboard shortcut is a quick undo feature that reverses the last action you took, restoring the deleted folder.
- Contextual Menu Option: Alternatively, you can right-click inside the folder's original location or on the desktop (if the folder was deleted from there) and select "Undo Delete" from the context menu. This option will also reverse the deletion if it is one of the most recent actions performed.
Advanced Recovery Methods for Permanently Deleted Folders
Using File History to Restore Previous Versions
File History is a built-in Windows feature that allows you to revert to earlier versions of files and folders, providing a lifeline for recovering permanently deleted data. Here's how to use it:
- Ensure File History is Enabled: Before you can restore files, File History must be active on your Windows 10 system. You can check this by going to "Settings" > "Update & Security" > "Backup." Ensure that a backup drive is set, and File History is turned on.
- Navigate to the Folder's Previous Location: Go to the location where the folder was originally stored. This is necessary because File History saves the folder versions based on their original paths.
- Access Previous Versions: Right-click on the empty space within the folder's original directory, not on any file or leftover item, and select "Restore previous versions." This will open a dialog showing all available snapshotted versions of that folder path.
- Choose and Restore the Desired Version: In the list of snapshots, browse different dates and versions to find the one that contains your missing folder. Once you've identified the appropriate version, select it and click "Restore." This action will recover the folder back to its original location with all contents as they were at the time of the snapshot.
Employing Data Recovery Software
Introduction to DiskInternals Partition Recovery™
At some point, after you have tried all the methods explained above and none worked for you, the best reliable option is to use a third-party data recovery solution like the DiskInternals Partition Recovery app. This data recovery solution works on all Windows OS computers and features an intuitive interface – integrating a Wizard interface – that makes it easy for virtually any computer literate to use the software.
DiskInternals Partition Recovery™ is an advanced data recovery software designed to help users retrieve lost files from deleted or damaged partitions, positioning itself as a crucial tool for both individual and professional use. Here’s a detailed look at its features and capabilities:
- Comprehensive Data Recovery: The software is engineered to handle a wide range of recovery scenarios, from accidental deletions of folders to complex data loss situations involving partition corruption or disk formatting. This makes it incredibly versatile and essential for users who encounter data loss across different storage environments.
- Support for Multiple File Systems: DiskInternals Partition Recovery™ supports a variety of file systems including NTFS, FAT, and exFAT. This broad compatibility means it can recover data from most hard drives, SSDs, USB drives, and memory cards, irrespective of the file system used, making it suitable for practically any device that stores data.
- User-Friendly Interface: Despite its robust functionality, the software is designed with a user-friendly interface that simplifies the recovery process. The intuitive layout and guided recovery wizard make it accessible even to users with minimal technical expertise, while professionals can leverage its more advanced features for deeper data retrieval needs.
- Advanced Scanning Options: DiskInternals Partition Recovery™ offers both quick and deep scan options. The quick scan is ideal for recent deletions, swiftly identifying recoverable data, whereas the deep scan is suited for more challenging recovery tasks, searching the disk thoroughly for file remnants even after severe damage or extensive overwriting.
- Preview Before Recovery: One of its standout features is the ability to preview files before proceeding with recovery. This ensures that users can verify the integrity of their data and select only the necessary files to restore, saving time and ensuring precision in the recovery process.
- Step-by-Step Recovery Wizard: The built-in recovery wizard guides users through each stage of the recovery process, from selecting the drive to recovering specific files, thus reducing the complexity typically associated with data recovery software.
- Reliability and Support: The software includes comprehensive documentation and customer support, ensuring that users can access help when needed. This level of support is essential, particularly in professional environments where data integrity and timely recovery are paramount.
With DiskInternals Partition Recovery tool, you can recover lost folders and files, regardless of how they were deleted from the computer. More so, you won’t have to pay for the PRO version until you confirm that your lost files have been recovered. There’s a built-in File Preview engine that lets you preview the recovered files for confirmation before upgrading your software to get them saved on your PC or remote storage. Here’s a guide to using DiskInternals Partition Recovery.
Step-by-Step Guide to Recovering Folders with DiskInternals Partition Recovery™
- Step One: Install the Partition Recovery software on your computer system and launch it to recover your lost folders. If the folder was lost from an external drive, connect the drive to the computer where the DiskInternals software is installed.
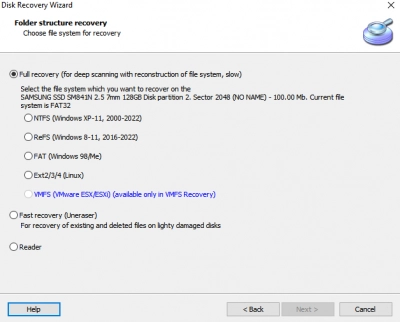
- Step Two: Select the drive where the lost folder was previously located and choose a data recovery mode: Fast Recovery or Full Recovery.
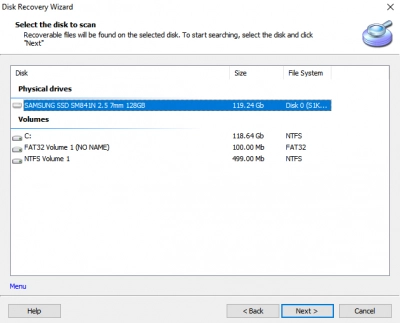
- Third Step: Full recovery takes more time but recovers deeply because it goes deeper into the drive to find lost files. When the scanning is complete, you’d see the deleted files appear with a red asterisk to indicate they are the files you need to recover.
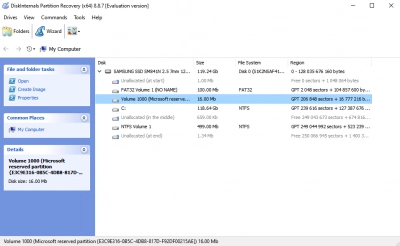
- Fourth Step: Preview the recovered files to confirm they are the ones you want to get back. Simply select the file(s) and click on the “Preview” option.
- Fifth Step: The recovered files must be saved to a new storage location and not the same drive where they got lost from. Interestingly, you can export the files to remote storage via FTP.
Note: DiskInternals Partition Recovery uses an advanced recovery algorithm trusted by IT experts for more than 15 years.
Video Tutorial on How to Recover Deleted Files on Windows 11/10/8/7 Easily
Preventative Measures to Safeguard Your Data
Regular Backups Using Windows File History
Windows File History provides a built-in backup solution that can help prevent data loss by routinely saving copies of your files:
- Connecting an External Drive: Begin by connecting an external hard drive or ensuring a network drive is accessible. This drive will store your backup copies and needs to have enough space to accommodate your files.
- Enabling File History: Navigate to "Settings" > "Update & Security" > "Backup" and turn on File History. Select your external drive as the backup destination. This ensures your important data is duplicated and safe from local hardware failures.
- Customizing Backup Settings: Within File History, you can customize how frequently backups occur and how long versions are retained. Choosing a higher frequency and longer retention can protect against a wide range of data loss scenarios, though it's essential to balance this with available storage.
Utilizing Cloud Storage Solutions
Cloud storage services offer robust and flexible data protection by automatically syncing and backing up files across devices:
- Automatic Synchronization: Services like OneDrive, Google Drive, and Dropbox provide seamless file synchronization, ensuring your latest work is backed up in the cloud. Any changes made to files on one device automatically reflect across all synced devices.
- Secure Offsite Backup: Storing data in the cloud ensures another layer of security, safeguarding your files against local disasters or theft. Ensure these services are set to automatically backup critical folders, and utilize versioning features where available to recover from accidental edits or deletions.
Implementing System Restore Points
System Restore in Windows offers a useful tool to recover from system-level issues without impacting personal files:
- Enabling System Restore: To activate, search for "Create a restore point" in the Windows search bar and select it. Enable the feature on your system drive. Windows will now periodically create snapshots of essential system files and settings.
- Using Restore Points: In the event of software issues or system instability, these restore points can be used to revert your system to a previous state, potentially resolving the issue while preserving your personal data stored elsewhere. It’s an effectively preemptive measure against incompatible software or system updates causing disruptions.
By incorporating these preventative steps, you can significantly minimize the risk of data loss and ensure that your important information remains secure and readily accessible, even amidst unexpected events.
Conclusion
Losing a folder in Windows 10 can be unsettling, but with the right approach, recovery is often possible. By understanding the difference between temporary and permanent deletions, and utilizing both immediate and advanced recovery methods, you can efficiently restore lost data. DiskInternals Partition Recovery™ offers a reliable option for more complex scenarios involving partition loss. As always, the best strategy is preventative. Regular backups using Windows File History, cloud storage solutions like OneDrive or Dropbox, and implementing system restore points all serve to protect your data against unforeseen losses. By embedding these practices into your routine, you can ensure greater security and peace of mind for your invaluable files.
FAQ
What to do if I accidentally moved a folder and can't find it Windows 10?
If you accidentally moved a folder and can't find it in Windows 10, you can try the following steps:
1. Check the Recycle Bin: If you moved the folder to a different location on the same drive, it might have ended up in the Recycle Bin. Open the Recycle Bin and search for the folder.
2. Use the Windows Search: Click on the Start menu and type the name of the folder in the search bar. If the folder was moved to a different location on the same drive, it should show up in the search results.
3. Check other locations: If the above steps do not work, the folder may have been moved to a different drive or location. Check other drives or folders on your computer to see if the folder is located there.
4. Use data recovery software: If the above steps do not work, you can try using data recovery software like DiskInternals Partition Recovery or DiskInternals Uneraser to recover the lost folder.
Where is my deleted folder on Windows 10?
When you delete a folder on Windows 10, it is typically moved to the Recycle Bin. The Recycle Bin is a temporary storage area for deleted files and folders on your computer. You can find the Recycle Bin on your desktop or by searching for it in the Windows search bar.
To restore a deleted folder from the Recycle Bin, you can simply right-click on the folder and select "Restore." If the folder was deleted from the Recycle Bin or you have emptied the Recycle Bin, you may still be able to recover the folder using a data recovery tool.
How to recover deleted folder from desktop?
1. Check the Recycle Bin
2. Use the Windows Search
3. Check other locations
4. Use data recovery software
Can I recover a folder deleted a long time ago?
Recovering a folder deleted a long time ago can be challenging but is sometimes possible depending on several factors. If you haven't overwritten the space the folder occupied, you might use recovery software like DiskInternals Partition Recovery™ to find and restore it. Checking backups, such as through Windows File History or cloud storage, would be the most straightforward method if those were active at the time of deletion. The success of recovery largely depends on how much new data has been written to the drive since the folder was deleted, as overwriting reduces the chance of recovery. Ultimately, proactive measures like regular backups and cloud storage synchronization significantly enhance your ability to recover data from long-lost deletions.Is data recovery software safe to use?
Data recovery software is generally safe to use, provided you choose reputable and well-reviewed options. Trusted software usually adheres to industry standards, ensuring that it doesn't alter the data on your drive during the recovery process. However, the incorrect use of certain advanced features may inadvertently cause data loss, so it's important to follow provided instructions carefully. It's advisable to download such software from official websites to avoid malware or unwanted bundled software. Additionally, using the software sooner rather than later increases the likelihood of successful recovery without further data compromise.Are there free options for data recovery?
Yes, there are free data recovery software options available that can effectively help recover lost files. Tools like PhotoRec, and TestDisk offer basic recovery features without cost. While these free tools can be quite helpful, they may have limitations compared to their paid counterparts, such as less comprehensive scanning capabilities or restrictions on file types recoverable. It's important to research and select free software that suits your specific recovery needs and ensure it's downloaded from a reputable source. Free options can be a good starting point, though for more complex recoveries, investing in a premium tool might be necessary.What should I do if I can't recover my deleted folder?
If you're unable to recover a deleted folder, start by ensuring that no further data is written to the drive to avoid overwriting any remaining traces. Double-check backups, including cloud storage and external drives, as they may hold copies of the lost folder. Consider reaching out to a professional data recovery service, especially if the folder contains critical data, as they have specialized tools and expertise. Reflect on implementing stronger data protection measures, like regular backups, to prevent future data loss. Lastly, it might be an opportunity to reassess how you organize and store important files for increased security.
